第1章 torch.nn简介
1.1 torch.nn相关库的导入
#环境准备 import numpy as np # numpy数组库 import math # 数学运算库 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 画图库 import torch # torch基础库 import torch.nn as nn # torch神经网络库 import torch.nn.functional as F
1.2 torch.nn概述
Pytorch提供了几个设计得非常棒的模块和类,比如 torch.nn,torch.optim,Dataset 以及 DataLoader,来帮助程序员设计和训练神经网络。
nn是Neural Network的简称,帮助程序员方便执行如下的与神经网络相关的行为:
(1)创建神经网络
(2)训练神经网络
(3)保存神经网络
(4)恢复神经网络
其包括如下五大基本功能模块:
- nn.Parameter
- nn.Linear
- nn.functional
- nn.Module
- nn.Sequential
第2章 nn.Linear类(全连接层)
2.1 函数功能
创建一个多输入、多输出的全连接层
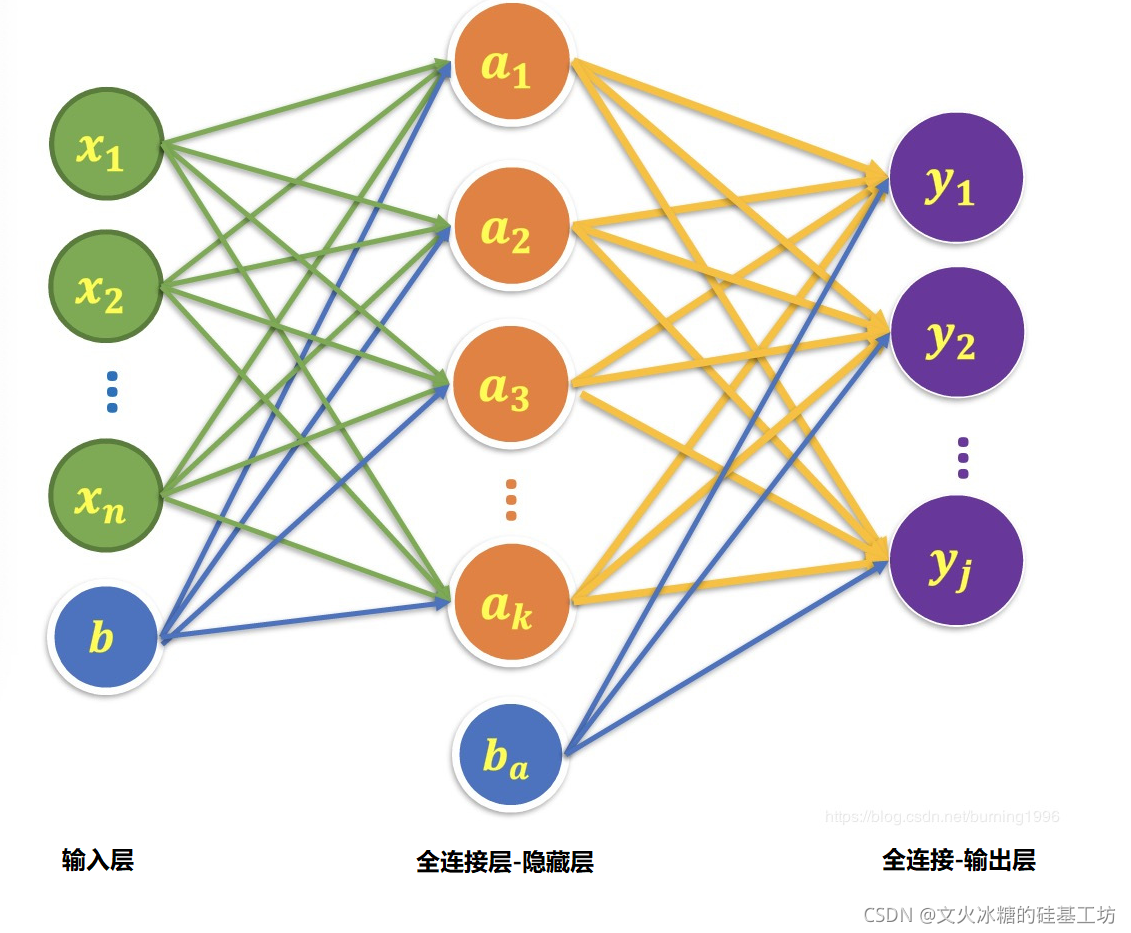
2.2 函数说明
- in_features:
指的是输入的二维张量的大小,即输入的[batch_size, size]中的size。
in_features的数量,决定的参数的个数 Y = WX + b, X的维度就是in_features,X的维度决定的W的维度, 总的参数个数 = in_features + 1
- out_features:
指的是输出的二维张量的大小,即输出的二维张量的形状为[batch_size output_size]。
out_features的数量,决定了全连接层中神经元的个数,因为每个神经元只有一个输出。
多少个输出,就需要多个个神经元。
从输入输出的张量的shape角度来理解,相当于一个输入为[batch_size, in_features]的张量变换成了[batch_size, out_features]的输出张量。
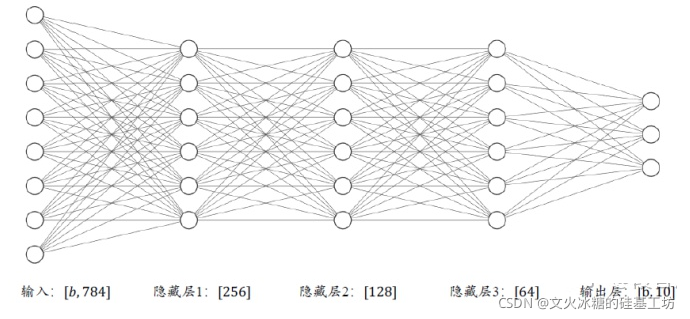
2.3 多个全连接层构建全连接网络
2.4 使用nn.Linear类创建全连接层
# nn.Linear
# 建立单层的多输入、多输出全连接层
# in_features由输入张量的形状决定,out_features则决定了输出张量的形状
full_connect_layer = nn.Linear(in_features = 28 * 28 * 1, out_features = 3)
print("full_connect_layer:", full_connect_layer)
print("parameters :", full_connect_layer.parameters)
# 假定输入的图像形状为[64,64,3]
x_input = torch.randn(1, 28, 28, 1)
# 将四维张量转换为二维张量之后,才能作为全连接层的输入
x_input = x_input.view(1, 28 * 28 * 1)
print("x_input.shape:", x_input.shape)
# 调用全连接层
y_output = full_connect_layer(x_input)
print("y_output.shape:", y_output.shape)
print("y_output:", y_output)
输出结果:
full_connect_layer: Linear(in_features=784, out_features=3, bias=True) parameters : <bound method Module.parameters of Linear(in_features=784, out_features=3, bias=True)> x_input.shape: torch.Size([1, 784]) y_output.shape: torch.Size([1, 3]) y_output: tensor([[-0.2892, -0.3084, 0.9027]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
第3章 nn.functional(常见函数)
3.1 nn.functional概述
nn.functional定义了创建神经网络所需要的一些常见的处理函数。如没有激活函数的神经元,各种激活函数等。
- 包含 torch.nn 库中所有函数,包含大量 loss 和 activation function
- torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None,stride=1,padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1)
- nn.functional.xxx是函数接口
- nn.functional.xxx无法与 nn.Sequential 结合使用
- 没有学习参数的(eg.maxpool, loss_func, activation func)等根据个人选择使用 nn.functional.xxx或 nn.Xxx
- 需要特别注意dropout层
3.2 nn.functional函数分类
Pytorch中文网,详细说明了各种函数及参数类型:https://ptorch.com/docs/1/functional#non-linear-activation-functions
(1)神经元处理函数
如Convolution、pooling、Normalization、Dropout、损失函数等
(2)激活函数
3.3 激活函数的案例
(1)relu案例
# nn.functional.relu( ) print(y_output) out = nn.functional.relu(y_output) print(out.shape) print(out)
输出结果:
tensor([[ 0.1023, 0.7831, -0.2368]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>) torch.Size([1, 3]) tensor([[0.1023, 0.7831, 0.0000]], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
(2)sigmoid案例
# nn.functional.sigmoid( ) print(y_output) out = nn.functional.sigmoid(y_output) print(out.shape) print(out)
输出结果:
tensor([[ 0.1023, 0.7831, -0.2368]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>) torch.Size([1, 3]) tensor([[0.5255, 0.6863, 0.4411]], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward>)
此处输出中,tensor([[0.5255, 0.6863, 0.4411]], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward>) 中的grad_fn为梯度函数,方便进行反向传播:
https://blog.csdn.net/zphuangtang/article/details/112788037
https://geek-docs.com/pytorch/pytorch-questions/303_pytorch_in_pytorch_what_exactly_does_the_grad_fn_attribute_store_and_how_is_it_used.html
第4章 nn.xxx和nn.functional.xxx比较
4.1 相同点
nn.Xxx和nn.functional.xxx的实际功能是相同的,即nn.Conv2d和nn.functional.conv2d都是进行卷积,nn.Dropout和nn.functional.dropout都是进行dropout- 运行效率也是近乎相同。
4.2 不同点
- 形式看:nn.functional.xxx是小写字母开头,nn.Xxx中的函数是大写字母开头。
- nn.functional.xxx是API函数接口,而nn.Xxx是对原始API函数nn.functional.xxx的类封装。
- 所有nn.Xxx都继承于于共同祖先nn.Module。这一点导致nn.Xxx除了具有nn.functional.xxx功能之外,内部附带了nn.Module相关的属性和方法,例如train(), eval(),load_state_dict, state_dict 等。
- nn.Xxx继承于nn.Module, 能够很好的与nn.Sequential结合使用, 而nn.functional.xxx无法与nn.Sequential结合使用。
- nn.Xxx 需要先实例化并传入参数,然后以函数调用的方式调用实例化的对象并传入输入数据。nn.functional.xxx同时传入输入数据和weight, bias等其他参数 。
- nn.Xxx不需要你自己定义和管理weight;而nn.functional.xxx需要你自己定义weight,每次调用的时候都需要手动传入weight, 不利于代码复用。
参考:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/66782101/answer/579393790
第5章 nn.Parameter类
5.1 nn.Parameter概述
Parameter实际上也是Tensor,也就是说是一个多维矩阵,是Variable类中的一个特殊类。
当我们创建一个model时,nn会自动创建相应的参数parameter,并会自动累加到模型的Parameter 成员列表中。
反向传播需要被optimizer更新
5.2 单个全连接层中参数的个数
in_features的数量,决定的参数的个数 Y = WX + b, X的维度就是in_features,X的维度决定的W的维度, 总的参数个数 = in_features + 1
out_features的数量,决定了全连接层中神经元的个数,因为每个神经元只有一个输出。
多少个输出,就需要多少个神经元。
总的W参数的个数= in_features * out_features
总的b参数的个数= 1 * out_features
总的参数(W和B)的个数= (in_features + 1) * out_features
5.3 使用参数创建全连接层代码案例
# nn.functional.linear( )
x_input = torch.Tensor([1., 1., 1.])
print("x_input.shape:", x_input.shape)
print("x_input :", x_input)
print("")
Weights1 = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(3))
print("Weights.shape:", Weights1.shape)
print("Weights :", Weights1)
print("")
Bias1 = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(1))
print("Bias.shape:", Bias1.shape)
print("Bias :", Bias1)
print("")
Weights2 = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(3))
print("Weights.shape:", Weights2.shape)
print("Weights :", Weights2)
print("\nfull_connect_layer")
full_connect_layer = nn.functional.linear(x_input, Weights1)
print(full_connect_layer)
输出:
x_input.shape: torch.Size([3]) x_input : tensor([1., 1., 1.]) Weights.shape: torch.Size([3]) Weights : Parameter containing: tensor([0.3339, 0.7027, 0.9703], requires_grad=True) Bias.shape: torch.Size([1]) Bias : Parameter containing: tensor([0.4936], requires_grad=True) Weights.shape: torch.Size([3]) Weights : Parameter containing: tensor([0.0000e+00, 1.8980e+01, 1.1210e-44], requires_grad=True) full_connect_layer tensor(2.0068, grad_fn=<DotBackward>)
第6章 nn.Module类
这是一个抽象概念,既可以表示神经网络中的某个层(layer),也可以表示一个包含很多层的网络
https://blog.csdn.net/xw555666/article/details/135910015
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27825451/article/details/90550890
pytorch中nn.module如何自动调用forward()方法:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53229076/article/details/140238691
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/651139584
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/366461413
第7章 利用nn.Sequential类创建神经网络(继承与nn.Module类)
7.1 概述
A sequential container. Modules will be added to it in the order they are passed in the constructor. Alternatively, an ordered dict of modules can also be passed in.
nn.Sequential是一个有序的容器,该类将按照传入构造器的顺序,依次创建相应的函数,并记录在Sequential类对象的数据结构中,同时以神经网络模块为元素的有序字典也可以作为传入参数。
因此,Sequential可以看成是有多个函数运算对象,串联成的神经网络,其返回的是Module类型的神经网络对象。
7.2 以列表的形式,串联函数运算,构建串行执行的神经网络
print("利用系统提供的神经网络模型类:Sequential,以参数列表的方式来实例化神经网络模型对象")
# A sequential container. Modules will be added to it in the order they are passed in the constructor.
# Example of using Sequential
model_c = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(28*28, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 10),
nn.Softmax(dim=1)
)
print(model_c)
print("\n显示网络模型参数")
print(model_c.parameters)
print("\n定义神经网络样本输入")
x_input = torch.randn(2, 28, 28, 1)
print(x_input.shape)
print("\n使用神经网络进行预测")
y_pred = model.forward(x_input.view(x_input.size()[0],-1))
print(y_pred)
输出:
利用系统提供的神经网络模型类:Sequential,以参数列表的方式来实例化神经网络模型对象 Sequential( (0): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True) (1): ReLU() (2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True) (3): Softmax(dim=1) ) 显示网络模型参数 bound method Module.parameters of Sequential( (0): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True) (1): ReLU() (2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True) (3): Softmax(dim=1) ) 定义神经网络样本输入 torch.Size([2, 28, 28, 1]) 使用神经网络进行预测 tensor([[-0.1526, 0.0437, -0.1685, 0.0034, -0.0675, 0.0423, 0.2807, 0.0527, -0.1710, 0.0668], [-0.1820, 0.0860, 0.0174, 0.0883, 0.2046, -0.1609, 0.0165, -0.2392, -0.2348, 0.1697]], grad_fn=)
7.3 以字典的形式,串联函数运算,构建串行执行的神经网络
# Example of using Sequential with OrderedDict
print("利用系统提供的神经网络模型类:Sequential,以字典的方式来实例化神经网络模型对象")
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([('h1', nn.Linear(28*28, 32)),
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('out', nn.Linear(32, 10)),
('softmax', nn.Softmax(dim=1))]))
print(model)
print("\n显示网络模型参数")
print(model.parameters)
print("\n定义神经网络样本输入")
x_input = torch.randn(2, 28, 28, 1)
print(x_input.shape)
print("\n使用神经网络进行预测")
y_pred = model.forward(x_input.view(x_input.size()[0],-1))
print(y_pred)
输出:
利用系统提供的神经网络模型类:Sequential,以字典的方式来实例化神经网络模型对象
Sequential(
(h1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True)
(relu1): ReLU()
(out): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=1)
)
显示网络模型参数
bound method Module.parameters of Sequential(
(h1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True)
(relu1): ReLU()
(out): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=1)
)
定义神经网络样本输入
torch.Size([2, 28, 28, 1])
使用神经网络进行预测
tensor([[0.1249, 0.1414, 0.0708, 0.1031, 0.1080, 0.1351, 0.0859, 0.0947, 0.0753,
0.0607],
[0.0982, 0.1102, 0.0929, 0.0855, 0.0848, 0.1076, 0.1077, 0.0949, 0.1153,
0.1029]], grad_fn=)
第8章 自定义神经网络模型类(继承于Module类)
# 定义网络模型:带relu的两层全连接神经网络
print("自定义新的神经网络模型的类")
class NetC(torch.nn.Module):
# 定义神经网络
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(NetC, self).__init__()
self.h1 = nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.out = nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
#定义前向运算
def forward(self, x):
# 得到的数据格式torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])需要转变为(64,784)
x = x.view(x.size()[0],-1) # -1表示自动匹配
h1 = self.h1(x)
a1 = self.relu1(h1)
out = self.out(a1)
a_out = self.softmax(out)
return out
print("\n实例化神经网络模型对象")
model = NetC(28*28, 32, 10)
print(model)
print("\n显示网络模型参数")
print(model.parameters)
print("\n定义神经网络样本输入")
x_input = torch.randn(2, 28, 28, 1)
print(x_input.shape)
print("\n使用神经网络进行预测")
y_pred = model.forward(x_input)
print(y_pred)
输出:
自定义新的神经网络模型的类 实例化神经网络模型对象 NetC( (h1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True) (relu1): ReLU() (out): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True) (softmax): Softmax(dim=1) ) 显示网络模型参数 <bound method Module.parameters of NetC( (h1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=32, bias=True) (relu1): ReLU() (out): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True) (softmax): Softmax(dim=1) )> 定义神经网络样本输入 torch.Size([2, 28, 28, 1]) 使用神经网络进行预测 tensor([[-0.3095, 0.3118, 0.3795, -0.2508, 0.1127, -0.2721, -0.3563, 0.3058, 0.5193, 0.0436], [-0.2070, 0.6417, 0.2125, -0.0413, 0.0827, 0.2448, -0.0399, 0.2837, 0.0052, -0.1834]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
参考链接: [Pytorch系列-30]:神经网络基础 – torch.nn库五大基本功能:nn.Parameter、nn.Linear、nn.functioinal、nn.Module、nn.Sequential-CSDN博客 https://blog.csdn.net/HiWangWenBing/article/details/120614234
https://ptorch.com/docs/1/functional#non-linear-activation-functions